本篇我们详细讲解一些常用的负载均衡算法。
什么是负载均衡
- 负载均衡指多台服务器以对称的方式组成一个服务器集合,每台服务器都具有等价的地位,都可以单独对外提供服务而无须其他服务器的辅助。
- 通过某种负载分担任务,将外部发送来的请求均匀分配到对称结构中的某一台服务器上,而接受到的请求的服务器独立地回应客户的请求。
- 负载均衡能够平均分配客户请求到服务器阵列,借此提供快速获取重要数据,解决大量并发访问服务问题,这种集群技术可以用最少的投资获得接近于大型主机的性能。
在分布式系统中,多台服务器同时提供一个服务,并统一到服务配置中心进行管理,消费者通过查询服务配置中心,获取到服务到地址列表,需要选取其中一台来发起RPC远程调用。如何选择,则取决于具体的负载均衡算法,对应于不同的场景,选择的负载均衡算法也不尽相同。负载均衡算法的种类有很多种,常见的负载均衡算法包括轮询法、随机法、源地址哈希法、加权轮询法、加权随机法、最小连接法、Latency-Aware等,应根据具体的使用场景选取对应的算法。
下面我们一起看下几种常见的负载均衡算法。
随机算法
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
type RandomBalance struct { //定义结构体
curIndex int
rss []string
}
//添加节点
func (r *RandomBalance) Add(params ...string) error {
if len(params) == 0 {
return errors.New("param len 1 at least")
}
addr := params[0]
r.rss = append(r.rss, addr)
return nil
}
//随机获取
func (r *RandomBalance) Next() string {
if len(r.rss) == 0 {
return ""
}
r.curIndex = rand.Intn(len(r.rss))
return r.rss[r.curIndex]
}
|
随机算法算是一种最简单的轮询算法,从一些服务器列表中随机挑选出一个服务器来进行负载操作,强调随机性。
但只是简单随机会有一些问题,如果我们有3台服务器,运算效率差距很大,第一台运算效率100分,第二台50分,第三台1分,那么我们简单随机的话,显然无法发挥第一台高性能服务器的优势,所以带权重的随机算法更加优秀。
加权随机
最简单的加权随机
最简单实现,我们可以创建一个List将所有的IP地址装入List,根据权重来选择装入几次IP地址,比如“198.168.0.1”这个IP地址的权重是2,那么就装入2次该IP地址
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
|
type WeightRandomBalance struct {
addrs []string
curIndex int
}
func (w *WeightRandomBalance) Add(addr string, weight int) error {
if weight <= 0 {
return errors.New("权重必须大于0")
}
for i := 0; i < weight; i++ {
w.addrs = append(w.addrs, addr)
}
return nil
}
func (w *WeightRandomBalance) Next() string {
if len(w.addrs) <= 0 {
return ""
}
w.curIndex = rand.Intn(len(w.addrs))
return w.addrs[w.curIndex]
}
|
优化简单加权随机
当权重很大的时候,将会存入很多次IP地址,耗费很大的空间 ,我们可以采用坐标映射的想法,具体如下:
其中A、B、C分别代表3个IP地址,权重分别为5、3、2
映射到坐标轴为 :0—5—8–10
随意在这个坐标轴取整数就可以确定其在哪个IP地址上 如:
1
|
offset = 7, 7在5---8这个区间里面,那么对应的就是B这台服务器
|
具体实现思路:
offset > 5; offset - 5; offset = 2;
offset < 3;
对应B
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
|
//参考 https://github.com/mroth/weightedrand
type WeightRandomBalance2 struct {
addrs []WeightRandomNode
totals []int
max int
}
type WeightRandomNode struct {
addr string
weight int
}
func NewWeightRandomBalance2(wn ...WeightRandomNode) WeightRandomBalance2 {
sort.Slice(wn, func(i, j int) bool {
return wn[i].weight < wn[j].weight
})
totals := make([]int, len(wn))
runningTotal := 0
for i, w := range wn {
runningTotal += w.weight
totals[i] = runningTotal
}
return WeightRandomBalance2{addrs: wn, totals: totals, max: runningTotal}
}
func (w *WeightRandomBalance2) Next() string {
r := rand.Intn(w.max) + 1 // 使用最大值获取随机数,避免超过范围,随机生成的数需要排除0,故加1
i := sort.SearchInts(w.totals, r) // 核心点该方法使用二分法,找到对应的下标,如果没有则为大于该数的+1 下标,可能为len(a)即数组长度。
return w.addrs[i].addr
}
|
轮询算法
简单顺序轮询
按照原来的顺序轮询服务器
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
|
type Round struct {
curIndex int
rss []string
}
func (r*Round) Add(params ...string) error{
if(len(params)==0){
return errors.New("至少需要1个参数")
}
addr:=params[0]
r.rss = append(r.rss,addr)
return nil
}
func (r*Round) Next() (string,error){
if(len(r.rss)==0){
return "" ,errors.New("不存在参数")
}
curElement:=r.rss[r.curIndex]
r.curIndex = (r.curIndex+1)%len(r.rss)
return curElement,nil
}
|
加权轮询
Nginx默认采用这种算法
假如有三台机器,A权重5,B权重1,C权重1
A: 5 B: 1 C: 1
这样的话,访问顺序为AAAAABC,这样的话对服务器A的压力比较大
如果按照离散的话,就不会有这样的问题,如下面这种顺序
AABACAA
这样不仅能使服务比较分散,也能保证权重,还能达到轮询的目的
具体过程如下:
初始化所有currentWeight=Weight
遍历所有的节点,使currentWeight=currentWeight+effectiveWeight
然后选中最大的currentWeight作为返回节点同时更新currentWeight=currentWeight-totalweight
| currentWeight+=weight |
max(currentWeight) |
result |
max(currentWeight)-=sum(weight)7 |
| 5,1,1 |
5 |
A |
-2,1,1 |
| 3,2,2 |
3 |
A |
-4,2,2 |
| 1,3,3 |
3 |
B |
1,-4,3 |
| 6,-3,4 |
6 |
A |
-1,-3,4 |
| 4,-2,5 |
5 |
C |
4,-2,-2 |
| 9,-1,-1 |
9 |
A |
2,-1,-1 |
| 7,0,0 |
7 |
A |
0,0,0 |
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
|
type WeightRoundRobinBalance struct {
curIndex int
rss []*WeightNode
rsw []int
}
type WeightNode struct {
addr string //服务器地址
weight int //权重值
currentWeight int //节点当前权重
effectiveWeight int //有效权重
}
func (r *WeightRoundRobinBalance) Add(params ...string) error {
if len(params) != 2 {
return errors.New("param len need 2")
}
//这里拿到权重
parInt, err := strconv.ParseInt(params[1], 10, 64)
if err != nil {
return err
}
//实例化具体的Node节点
node := &WeightNode{addr: params[0], weight: int(parInt)}
node.effectiveWeight = node.weight //权重值=有效权重
r.rss = append(r.rss, node) //append到服务器节点
return nil
}
//获取
func (r *WeightRoundRobinBalance) Next() string {
total := 0
var best *WeightNode //该次最优的ip
for i := 0; i < len(r.rss); i++ {
w := r.rss[i]
//统计所有有效权重之和
total += w.effectiveWeight
//变更节点临时权重为的节点临时权重+节点有效权重
w.currentWeight += w.effectiveWeight
//有效权重默认与权重相同,通讯异常时-1, 通讯成功+1,直到恢复到weight大小
if w.effectiveWeight < w.weight {
w.effectiveWeight++
}
//选择最大临时权重点节点
if best == nil || w.currentWeight > best.currentWeight {
best = w
}
}
if best == nil {
return ""
}
//变更临时权重为 临时权重-有效权重之和
best.currentWeight -= total
return best.addr
}
|
一致性哈希负载均衡
使用hash得到对应的服务器进行轮询,它符合以下特点:
算法原理如下
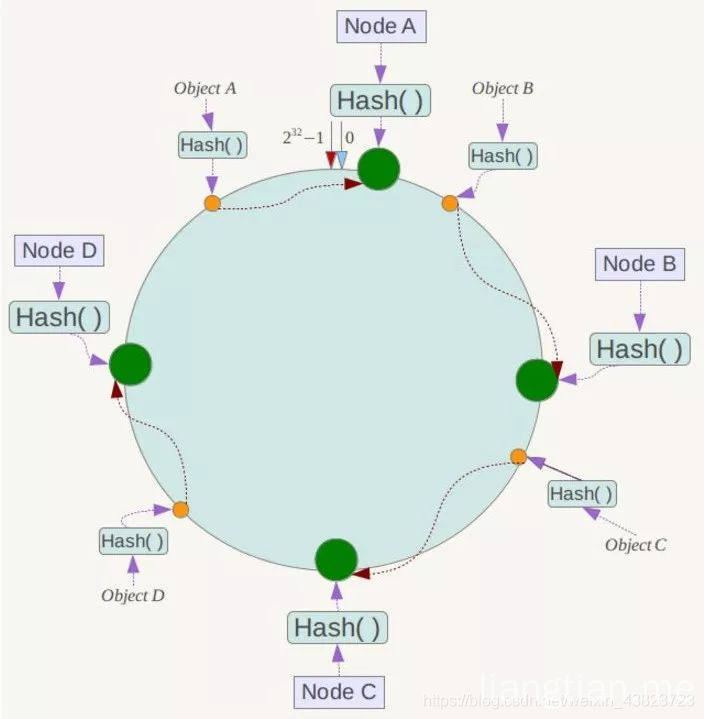
- 和一般hash表使用数组表示不太一样,一致性hash使用一个hash环来实现,因为一般的hash函数都可以返回一个int型的整数,所以将hash环平均分成2的32次方份,然后key的hashcode对2的32次方取模,一定会落到环上的一点。
各个节点(比如机器名称或者ip)的hashcode经过对2的32次方取模后,也一定会落到环上的一点
- 如果key和机器落到同一个位置,那么key存储到这个节点上,如果key没有落到某个机器节点上,那么沿着环顺时针寻找,将key存储到遇到的第一个节点上。
- 当删除一个节点(比如机器故障)时,获取被删除的节点上存储的key时,因为节点不存在了,所以沿着环继续顺时针走,会遇到下一个节点,这样就将原属于被删除节点的key移动到了下一个节点上,而所有属于其他节点的key并不受影响,无需重新分配。
- 增加一个节点时,也是同样的道理,这里不再详细描述。
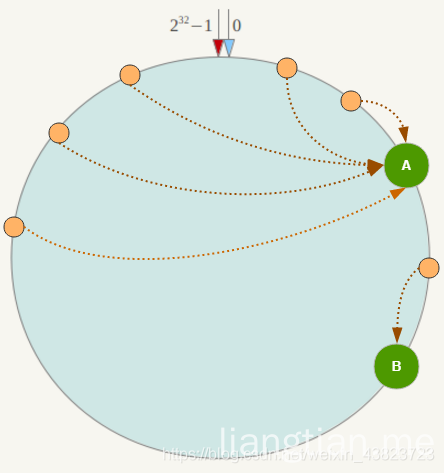
数据倾斜问题
一致性Hash算法在服务节点太少时,容易因为节点分部不均匀而造成数据倾斜(被缓存的对象大部分集中缓存在某一台服务器上)问题,例如系统中只有两台服务器,其环分布如下:
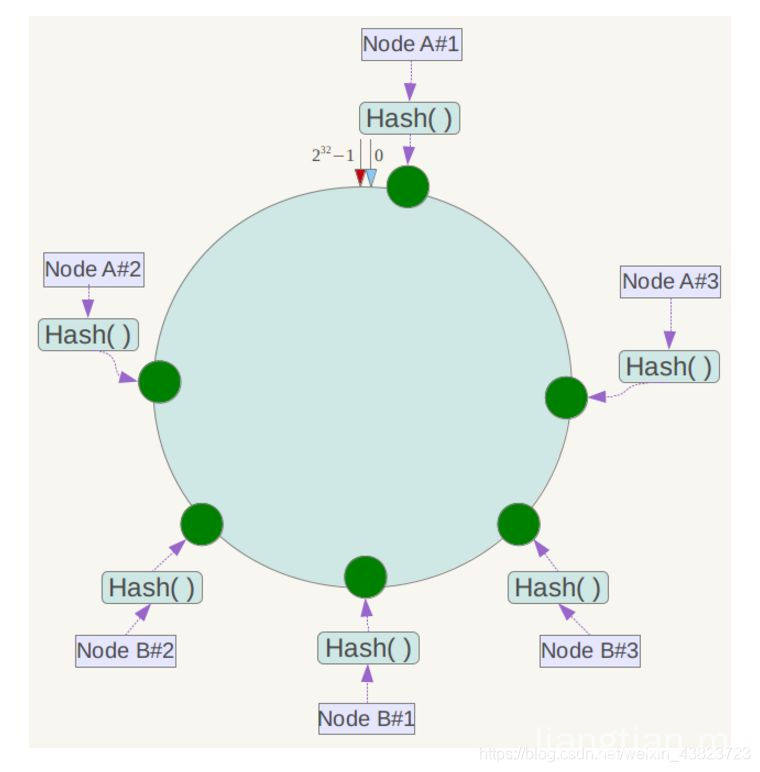
那么我们就需要添加虚拟节点了,例如上面的情况,可以为每台服务器计算三个虚拟节点,于是可以分别计算 “Node A#1”、“Node A#2”、“Node A#3”、“Node B#1”、“Node B#2”、“Node B#3”的哈希值,于是形成六个虚拟节点:
下面是代码:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
|
type Hash func(data []byte)uint32
type UInt32Slice []uint32
func (s UInt32Slice) Len() int {
return len(s)
}
type ConsistentHashBalance struct{
mux sync.RWMutex
hash Hash
replicas int //复制因子,即添加多少个虚拟节点
keys UInt32Slice//已经排序的节点hash切片
hashMap map[uint32]string
}
//利用复制因子和哈希函数创建一个一致性哈希算法
func NewConsistentHashBalance(replicas int,fn Hash) *ConsistentHashBalance {
m:=&ConsistentHashBalance{
replicas:replicas,
hash:fn,
hashMap:make(map[uint32]string),
}
if m.hash ==nil{
//最多32位
m.hash = crc32.ChecksumIEEE
}
return m
}
func (c*ConsistentHashBalance) Add (params ...string)error {
if len(params)==0{
return errors.New("参数个数不能为1")
}
addr:=params[0]
//因为要对哈希表进行操作所以需要加锁
c.mux.Lock()
defer c.mux.Unlock()
//根据复制因子计算所有虚拟节点的hash值存入keys中
//虚拟节点的实现
for i:=0;i<c.replicas;i++{
hash:=c.hash([]byte(strconv.Itoa(i)+addr))
c.keys = append(c.keys,hash)
c.hashMap[hash] = addr
}
//对keys进行排序,方便使用二分查找出对应的服务器节点(key)
sort.Sort(c.keys)
return nil
}
func (c*ConsistentHashBalance) Get(key string)(string,error) {
if c.keys.Len()==0{
return "",errors.New("没有代理转发服务器")
}
hash:=c.hash([]byte(key))
//通过二分查找最优节点 第一个服务器hash值大于数据hash值的为服务器节点
idx:=sort.Search(
len(c.keys),func(i int) bool{return c.keys[i]>=hash})
//数据hash值大于所有服务器节点hash值,把第一个服务器作为转发节点
if idx ==len(c.keys){
idx=0
}
c.mux.RLock()
defer c.mux.RUnlock()
return c.hashMap[c.keys[idx]],nil
}
|



